|
|
|
|
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |review |
References (more links) |
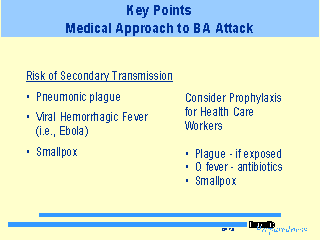
Although numerous biological agents exist, only a few pose a risk of person-to-person transmission to unprotected individuals. These agents include the respiratory form of plague, VHF (such as Ebola), and smallpox. Patients with these diseases should be
admitted with either respiratory droplet isolation (pneumonic plague and smallpox) or strict isolation (VHF). Most of the bacterial agents can be treated successfully with antibiotics (such as doxycycline and ciprofloxacin) if the disease is recognized
promptly and the drugs are administered early. These same two drugs can be administered orally as prophylaxis for known or imminent cases of biological agent contamination (such as anthrax, plague, and Q fever).
CDC has issued new recommendations for Biological and Chemical Terrorism on April 21, 2000 at www.cdc.gov/epo/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr4904a1.htm |