 |
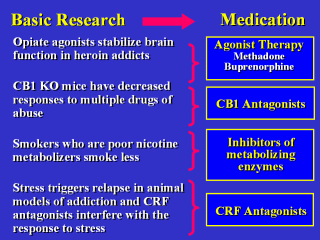
Basic research has led to the identification of
several potential medications for drug addiction. In addition to already
approved medications for treatment of opiate addiction (e.g., methadone,
buprenorphine), new approaches that target different aspects of addiction
are also being developed. For example, the cannabinoid receptor system (CB1)
is one that is being targeted for medications that reduce not only nicotine,
alcohol and other drug addictions, but obesity as well. Drug metabolism can
also be a factor in addiction susceptibility by altering the
pharmacokinetics and reinforcing effects of drugs. Smokers who are poor
metabolizers of nicotine smoke less and may be less vulnerable to
addiction--medications may be developed to take advantage of that quality.
Finally, animal models of relapse have allowed testing of medications that
inhibit triggers of drug seeking, including stress. Corticotropin releasing
factor (CRF) antagonists are examples as they inhibit the stress response
and the resultant drug seeking behavior. |
