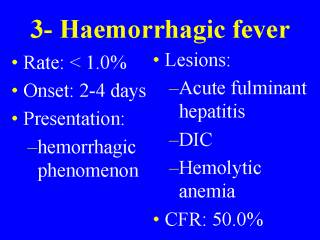
 |
RVF may also manifest itself as
haemorrhagic fever in less than 1.0% of RVF cases. Two to four days after the onset of
illness, the patient shows evidence of acute fulminant hepatitis with hepatic failure and
hepatorenal syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and haemolytic anaemia
with haemoglobin as low as 3gm/dL. The patient presents with haemorrhagic phenomenon as
haematemesis, melaena, purpuric rash and bleeding gums. Jaundice was also reported but in
low percentage of patients. Most patients with severe disease have elevated creatinine
phosphokinase enzyme (CPK). Despite the marked elevation of liver enzymes (AST, ALT) more
than triple fold, bilirubin level remains normal or slightly elevated and alkaline
phosphatase (ALP) remain normal. Patients with haemorrhagic fever may remain viraemic for
up to 10 days and case-fatality rate (CFR) is as high as 50.0%. |
