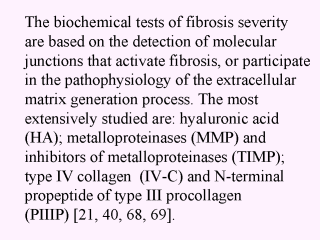
 |
In a typical early
study, Yamada et al. evaluated the diagnostic significance of fibrosis stage
determination with 36 patients having hemophilia and chronic hepatitis C (average age
31±9), using serum content of PIII P, IV-C and HA as liver fibrosis indicators. The
obtained results were compared with the conclusions obtained by means of liver biopsy. As
a result, a considerable correlation was observed between fibrosis stage 3-4 and HA, but
not the serum content of PIIIP and IV-C. All patients received standard interferon
therapy, the levels of the studied markers were evaluated 6 months after the therapy
cessation. The patients with a stable response had a positively reduced content of all
three serum markers compared to non-responders Thus, the HA marker can be used to diagnose
stages 3 and 4 of the fibrogenesis, as well the evaluation of the therapy effect. PIIIP,
as a marker of active fibrosis generation, reflected the intensity of the inflammation and
fibrogenesis rather than the fibrosis intensity [70], Considerable correlation of the
extracellular matrix markers with the degree of fibrosis intensity were reported in other
studies [21, 40, 65]. High diagnostic role of the concentration of HA, MMP, TIMP, PIIIP,
and IV-C for the differentiation of stage 1 and 2 fibrosis from stage 3 and 4 fibrosis was
demonstrated by Murawaki Y et al. [68]. The research by Shimizu I [21] demonstrated that the
level of P III P and IV-C correlated with iron concentration in the liver. Receiver
operating characteristic (ROC) curves were built to find out the relationship between
serum level of hyaluronic acid (HA), type III procollagen (PCIII), Nterminal procollagen
III peptide (PIIINP), laminin (LN), typeIV collagen (C-IV) analysed for by
radioimmunoassay, and hepatic fibrosis (114 chronic hepatitis patients) [69]. The
sensitivity of HA plus PIIINP was 55.1 %, it was the most sensitive combination. Combined
three or more than three indices that based on HA, the specificity was 100 % [69].
However, only PIIINP and PCIII had significant difference between G1 and G2 (PIIINP:
13.16+/-8.07 vs 8.32+/-5.09; PCIII: 164.22+/-65.69 vs 138.23+/-77.63) [69]. TIMP content
was specified as positively increasing at early stages of fibrosis, while the content of
PIIIP is positively increased at the stage of septal fibrosis [40]. PIIIP was in
considerable correlation with the necro-inflammatory processes in the liver and reflected
more the degree of inflammation than the stage of fibrosis [70, 71]. TIMP was suggested
for differential diagnostics of steatosis and fibrosis of the alcohol-affected liver [72].
|
