| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |review |
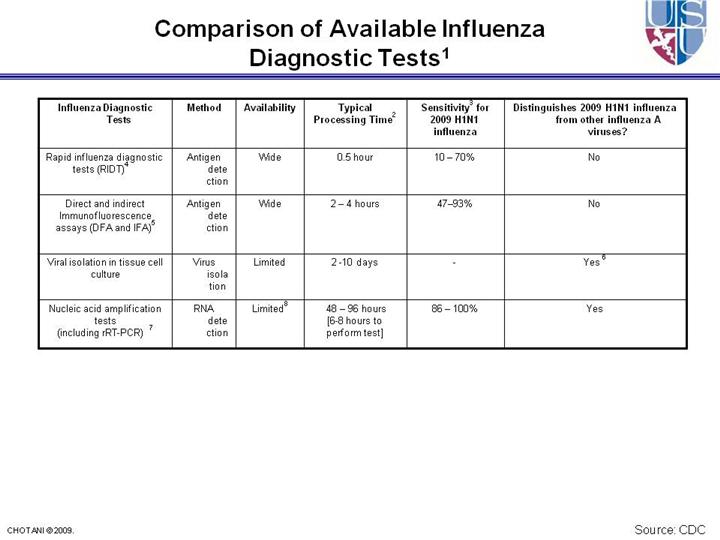 |
1 -
Serologic testing on paired acute- (within 1 week of illness onset) and
convalescent-phase (collected 2-3 weeks later) sera is limited to
epidemiological and research studies, is not routinely available through
clinical laboratories, and should not inform clinical decisions. 2 - The amount of time needed from specimen collection until results are available. 3 - Compared with rRT-PCR tests; rRT-PCR tests are compared to other testing modalities including other rRT-PCR assays. 4 - Rapid Influenza Diagnostic Tests include tests that are CLIA waived (can be performed in an outpatient setting) and tests that are moderately complex (can be performed only in a laboratory). Clinical specimens approved for RIDTs vary by test, and may not include all respiratory specimens. 5 - Performance of these assays relies heavily on laboratory expertise and requires a fluorescent microscope 6 - Requires additional testing on the viral isolate 7 - The performance of rRT-PCR assays specific for 2009 H1N1 influenza have not been established for bronchoalveolar lavage and tracheal aspirates. If testing these specimens for 2009 H1N1 influenza consider testing in parallel with a nasopharyngeal, nasal, or oropharyngeal swabs or a nasal aspirate. 8 - See discussion on available rRT-PCR assays at http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/guidance/diagnostic_tests.htm |