| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |review |
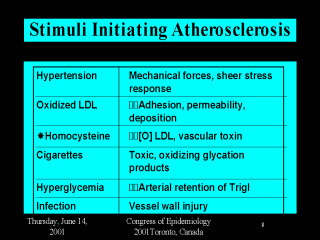 |
HTN: mechanical
forces change and injure the endothelium, promote formation of atherosclerosis. Activates
shear stress response elements in endothelial cells, upregulating genes for leukocyte
adhesion moleules (ICAM-1). Increased sheer stress reduces elements such as thrombomodulin essential for the normal anticoagulant state of the endothelium. [O] LDL elevated LDL increases atherogenicity. Increased expression of adhesion molecules increased permeability and deposition of lipid, triggers inflammatory response, causing migration of monocytes to the vessel wall.Macrophages become foam cells and the fatty streak. Homocysteine is a reactive amino acid toxic to vascular cells, potentiates the auto-oxidation of LDL.Proatherogenic and prothrombotic effect on blood vessels. Cigarette smoking : oxidizing and toxic glycation products are mediators assoc with proatherogenic and pro thrombotic condition. Nicotine and carbon monoxide have adverse effect on endothelial function, tone, hemostasis, lipid profile, & inflammatory cells. Hyperglycemia promotes the arterial wall retention of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, Also associated with a rise in ICAM-1 levels, reduced by insulin . Patients with NIDDM have increase in circulating proinflammatory or activated monocytes compared to nondiabetics. Infection injury to vessel wall results in migration of inflammatory cells and the release of pro inflammatory cytokines. Infection may ppt the initiation of plaque without needing to remain chronically to progress. Chronic infectio may lead to activagtion of resident T lymphocytes, enhancing a pro-inflammatory pro-thrombotic state. |
| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |review |