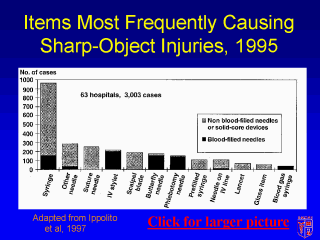
 |
It is important
to note the number of injuries caused by blood-filled vs. non-blood-filled devices. This
graph shows that the number of injuries caused by syringes is quite high. However, most of
those injuries did not involve needles which were filled with blood because most of these
injuries occurred during administration of some type of intramuscular or subcutaneous
injection. While these injuries still carry a risk for transmission of bloodborne
pathogens, the risk is not as high as with a blood-filled needle. Most of the injuries
caused by blood gas syringes, IV catheter stylets, butterfly needles, and phlebotomy
needles were high risk because the needles were filled with blood. |
