| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |review |
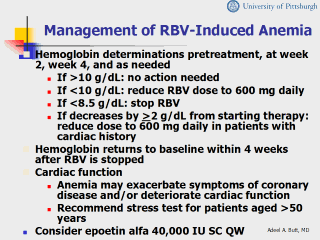 |
Conventional Management of Anemia for Patients Treated With RBV Depending on the severity of the anemia, the RBV dose may be reduced or eliminated. To date, the treatment of anemia in patients receiving combination therapy has included either dose reduction of therapy cessation. The following has served as a guide for practitioners managing HCV-therapy induced anemia. In patients without coronary heart disease: (1) Hb is >10 g/dL, no action needed; (2) Hb is 8.5-10 g/dL, reduce dose; and (3) Hb is 8.5 g/dL, stop RBV. In patients with coronary heart disease, consult a cardiologist (treat heart disease first). Hemoglobin should be evaluated frequently during the first few months of therapy. References Rebetron™ [package insert]. Kenilworth; NJ: Schering Corp; 1999. PEGASYS® Complete Product Information. Nutley, NJ: Hoffman-La Roche Inc; 2002. |