| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |49 |50 |51 |52 |53 |54 |review |
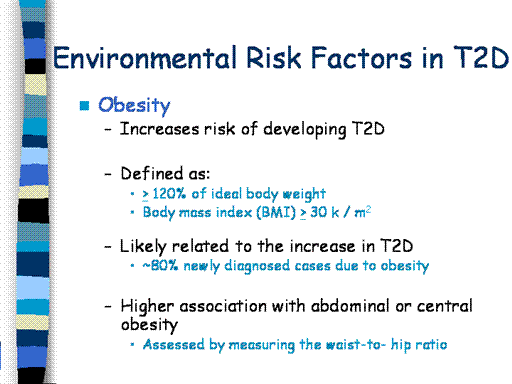 |
A major
environmental risk factor for T2D is obesity, defined by > 120%
ideal body weight or a body mass index (BMI) > 30 k/m2. Because obesity
increases risk for T2D, the tremendous increase in the
rates of T2D
in recent years has been attributed, primarily, to the dramatic risk in
obesity worldwide. It has been
estimated that approximately 80% of all new T2D cases are due to
obesity. This is true for
children and adults.
In addition to
general obesity, the distribution of body fat, estimated by the ratio of
the waist-to-hip circumferences (WHR).
WHR is a reflection of abdominal (central) obesity, which is more
strongly associated with T2D than standard measures, such as BMI.
|