| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |review |
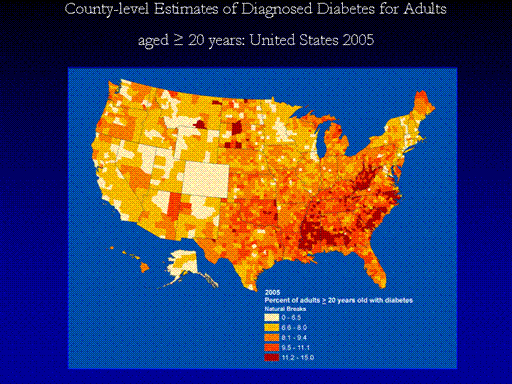 |
Methodology
The percent of
U.S. adults who are obese or who have diagnosed diabetes was determined
by using data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS,
available at
http://www.cdc.gov/brfss). An ongoing, yearly, state-based
telephone survey of the non-institutionalized adult population in each
state, the BRFSS provides state-specific information on behavioral risk
factors for disease and on preventive health practices. Respondents who
reported that a physician told them they had diabetes (other than during
pregnancy) were considered to have diagnosed diabetes. Self reported
weight and height were used to calculate body mass index (BMI): weight
in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. A BMI greater
than or equal to 30 was considered to be obese. Rates were age-adjusted
using the 2000 U.S. Standard Population.
|