Goal-line Technology
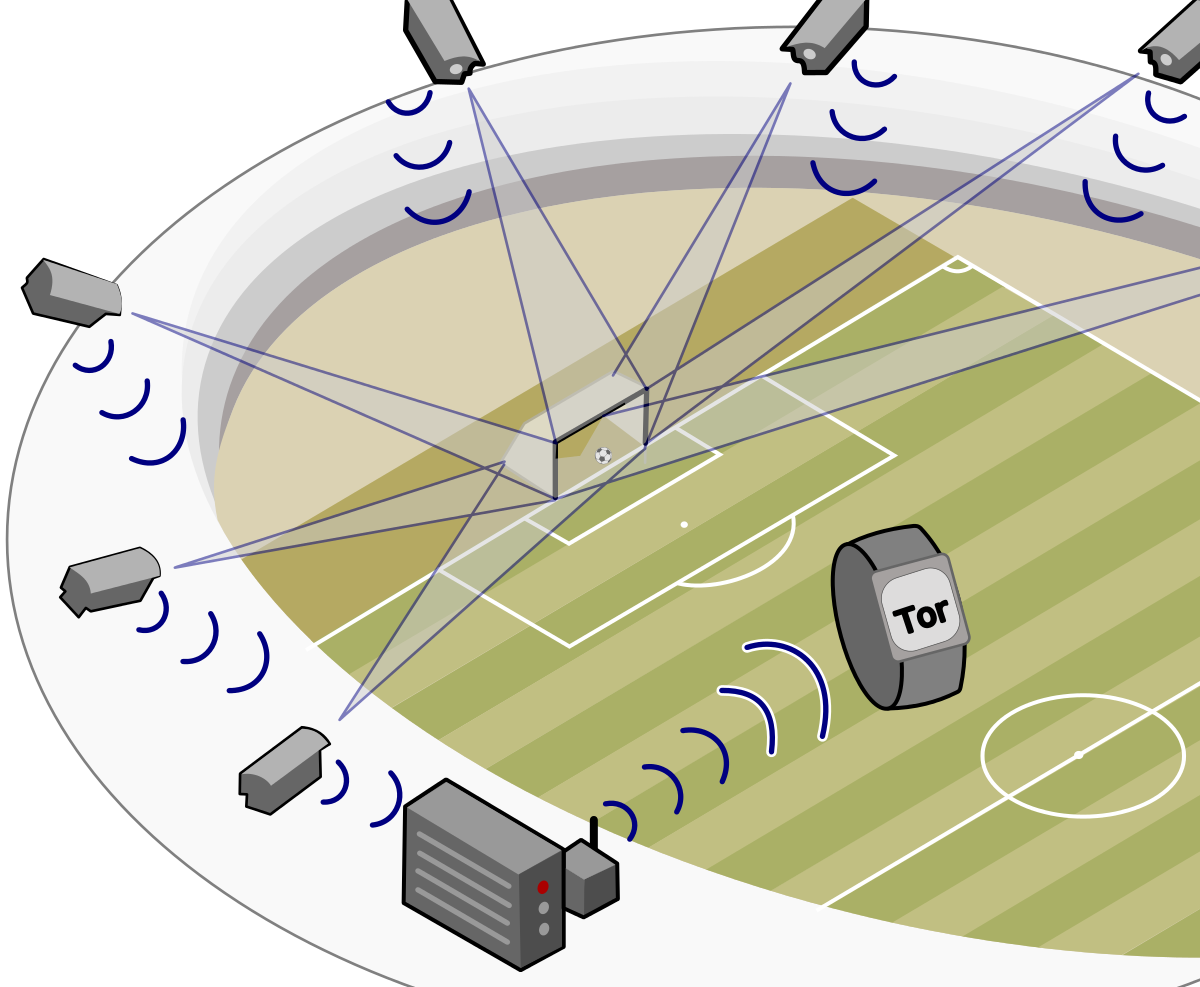
This technology detects goals and indicates whether they have been scored or not. It also helps when the human eye cannot determine whether the ball has crossed the goal line or not. This technology has two systems. The first system consists of 14 cameras that capture 500 cadre per second and send the images to a processing unit that tracks the triple coordinates of the ball; when the entire ball crosses the goal line, a signal is sent to the referee’s watch within one second.
Source: wikipedia.org
Watch: Goal-line technology is here (YouTube Video).
As for the second system, it depends on two magnetic fields of low frequencies. The first field is created in the goal area, and the other around the ball when it approaches the goal as a result of the built-in magnetic induction and the electronic circuit. The coils installed inside the goal capture the interaction between the two fields, and by measuring the change in the magnetic field, the position of the ball is identified from the goal-line, and the results are instantly sent to the referee’s watch making a slight vibration to notify them.
Watch: Goal-line technology: GoalRef explained (YouTube Video).
As such, this technique assists the referees in making decisions regarding offside balls, corner kicks, and throws in. Among the criteria that must be met are: extreme accuracy, simultaneous sending of signals, and sending signals only to match officials.
Video Assistant Referee (VAR)
This technology, commonly known as VAR, is used to limit refereeing errors; its team helps the match referee to make the correct decisions from within the video operating rooms. The team consists of the video referee, three assistants, and four workers to play the video clips that come from 33 cameras distributed throughout the stadium, and two cameras dedicated to monitoring offsides.
This technique is used in the cases that might change the match score. The team can communicate with the arena referees in case of a clear arbitration error; in return, the referee can also communicate with them for consultancy via radio waves through the headphones worn by the main referee. This technique is used in four cases: goals, penalties, direct red cards, and misidentification of card holders.

Source: www.foottheball.com
Watch: VAR – The System Explained (YouTube Video).
Performance Tracking
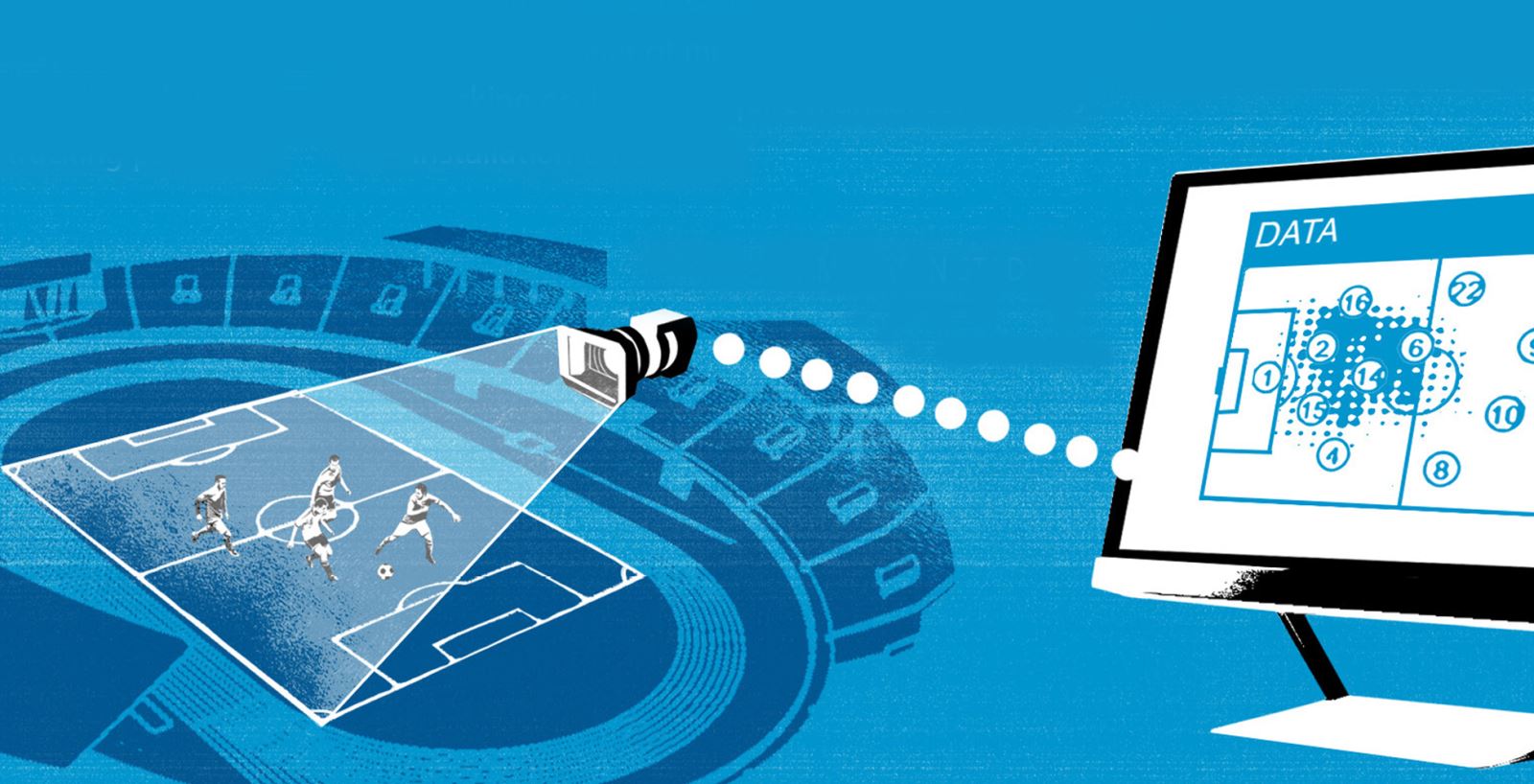
Using technology, smart watches, and GPS systems, the player's speed and steps, their resilience and concentration, strengths and weaknesses, fitness, health, and sleep pattern can be tracked. This data is used to supply the players performance platforms, which are platforms dedicated to displaying the players performance data. For example, the Wiscott platform helps clubs choose players; it also helps develop training programs for each player, and the coach can take appropriate decisions to protect the player from potential injuries.
 Source: www.fifa.com
Source: www.fifa.com
Sportswear
Technology was introduced in the sportswear industry to provide the player with amenities. These clothes are characterized by their ability to resist moisture, light weight when exposed to water, in addition to being waterproof. Some special techniques have been incorporated that absorb moisture from the body to evaporate from the surface of the shirt through the physical capillary action through which fluids move from the bottom up. Thanks to the development in lasers, shoes are also made specifically for the player from goatskin, kangaroo leather, or new polymeric materials, which are light, waterproof, and have a strong performance.
Watch: The Hidden Technology of Football (YouTube Video).
Technology continues to evolve, and so does football; we are expected to witness new technologies in the game, such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and holograms.
References