 |
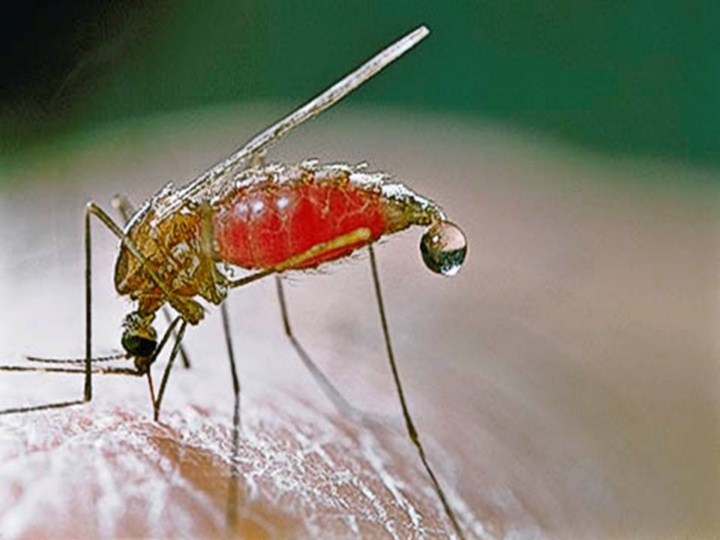
Malaria is naturally transmitted by the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito.
When a mosquito bites an infected person, a small amount of blood is taken,
which contains malaria parasites. These develop within the mosquito, and
about one week later, when the mosquito takes its next blood meal, the
parasites are injected with the mosquito's saliva into the person being
bitten. After a period of between two weeks and several months (occasionally
years) spent in the liver, the malaria parasites start to multiply within
red blood cells, causing symptoms that include fever, and headache. In
severe cases the disease worsens leading to hallucinations, coma, and death.
|
