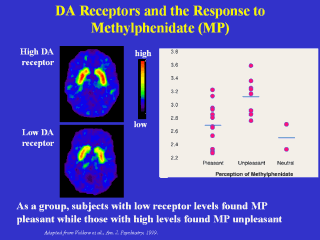
 |
The level of dopamine receptors in a personís
brain can influence whether he or she likes or dislikes the effects of a
drug. Because dopamine is involved in the rewarding effects of drugs of
abuse, it was hypothesized that normal individual variation in dopamine
receptors could influence a personís response to drug exposure. In this
study, human subjects were given the stimulant methylphenidate (Ritalin),
and their brainís were imaged using PET. Those subjects who had high levels
of dopamine receptors found the experience unpleasant; while those with
lower levels of dopamine found it pleasant. This suggests that individual
differences in a marker of dopamine function can influence an individualís
susceptibility to addiction. |
