Shallow Enhanced Analyzer
SEAN is a language-independent information extraction system expected to automatically
extract structured information, in the UNL Knowledge Base format, from unstructured
machine-readable natural language documents.
SEAN is part of a broader initiative, the KEYS (Knowledge Extraction sYStem), which
is intended to prove the efficacy of UNL as a language-independent knowledge representation
language, to be used in information retrieval and extraction. It is also a strategy
to automatically populate the UNL Knowledge Base.
SEAN falls under the category of UNL enconverters (such as EnCo and IAN), in the
sense that:
- It takes a natural language input and delivers an output in UNL, and
- It is language-independent, i.e., it has to be parameterized to the natural
language input through a dictionary and a grammar, to be provided as separate interpretable
files.
The main differences to the existing enconverting technologies are the following:
- SEAN is a multi-document analyzer: the input may be not only a single document
(as in Enco and IAN) but a whole collection of documents;
- SEAN is a word-driven analyzer: the unit of analysis is a word (and not a sentence
as in EnCo and IAN), to be provided by the user;
- SEAN is a shallow analyzer: the analysis targets the surface structure of natural
language sentences (and not the deep structure, as in EnCo and IAN).
The main consequences of such choices are that:
- As it provides a rather rough and partial analysis of the natural language input,
the results of SEAN are not appropriate for translation, but for information retrieval
and extraction only.
- As it reduces several different documents to a single graph whose nodes and edges
are weighted according to their frequency of occurrence, the results of SEAN cannot
be displayed as a UNL ordinary graph and should constitute, instead, a XML table
made out of UNL entities (relations and UWs), which is expected to be in the format
of and to be used as the UNL Knowledge Base.
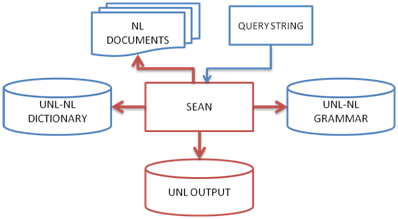
The general architecture of the system is depicted below:

The Arabic UNL Dictionary:
The Arabic UNL Dictionary The size of the main general dictionary reached 99,908
entries representing 52,572 universal concepts.