Dependent pronouns
They are less attached to a preceding word than the suffix pronouns, but can never stand as the first word of a sentence.
|
First Person Singular
|
I, me,
|
wi
|
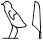 , , 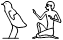 , , 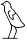 , , 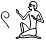
|
|
Second Person Masculine Singular
|
you, you
|
Tw, tw
|
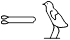 , , 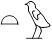
|
|
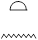
Second Person Feminine Singular
|
you, you
|
Tn, tn
|
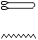 , , 
|
|
Third Person Masculine Singular
|
he, him, it
|
sw
|
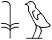 , , 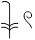
|
|
Third Person Feminine Singular
|
she, her, it
|
sy, st
|
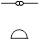
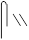 , , 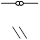 , ,  , , 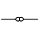 , , 
|
|
First Person Plural
|
we, us
|
n
|
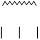
|
|
Second Person Plural
|
you, you
|
Tn, tn
|
 , ,  , , 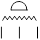 , , 
|
|
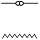
Third Person Plural
|
they, them
|
sn
|
 , ,  , , 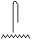 , , 
|
Notes
1) Determinatives in first person singular pronouns are written according to the gender of the speaker, and are occasionally omitted.
2) The third person plural pronoun  .sn is rarely used as an object and is replaced by
.sn is rarely used as an object and is replaced by 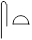 .st which is an early writing for the third person singular and plural independent pronouns.
.st which is an early writing for the third person singular and plural independent pronouns.
Uses of dependent pronoun:
a) Object in verbal sentences
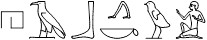
hAb.k wi
You send me.
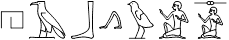
hAb wi s
The man sends me.
Note:
The object pronoun is placed before the noun subject.
b) Subject of a phrase with an predicate adverbial,
but it must follow a number of particles such as mk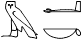 ، أو nn
، أو nn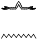 .:
.:
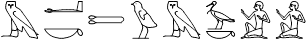
mk Tw m bAk. i
Behold, you are my servant.
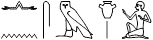
nn s(y) m ib.i
She is not in my heart.
c) Subject after predicate adjectival
This use is only confined to the second and third pronoun:
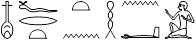
nfrt tn Hna .i
You are happy with me.
d) As a reflexive pronoun
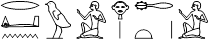
rdi.n (.i) wi Hr Xt. i
I placed myself on my body.