 |
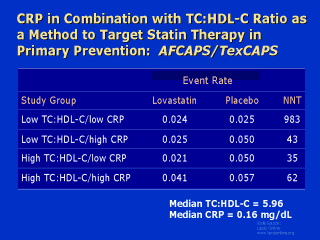
Similar results
were found using the total cholesterol:HDL-C ratio in AFCAPS/TexCAPS patients. Among
individuals with an above-median total cholesterol:HDL-C ratio, the NNT with lovastatin to
prevent 1 clinical event was within treatment guidelines regardless of the CRP level.
Among patients with below-median total cholesterol:HDL-C ratios, the NNT in those with an
elevated CRP was also quite comparable, whereas in those with a low level of CRP, the
absolute event rate was low and the efficacy of lovastatin was minimal, with the result
that the NNT was very large. On the basis of these data, our research group is currently
initiating a randomized clinical trial specifically addressing the efficacy of statin
therapy among individuals with low levels of cholesterol but elevated levels of CRP. Reference:
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Clearfield M, Downs JR, Weis SE, Miles JS, Gotto AM Jr, for the Air
Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study Investigators. Measurement of
C-reactive protein for the targeting of statin therapy in the primary prevention of acute
coronary events. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1959-1965.
Web
site |
