Click for larger image |
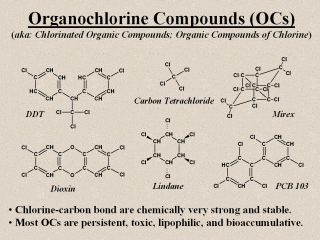
Organochlorine
compounds (OCs) are substances containing the chemical elements carbon
and chlorine, and in most cases also the element hydrogen.
They are also referred to as chlorinated organic compounds or as
organic compounds of chlorine. Well over 80,000 of these compounds are
man-made. Their chlorine-carbon bonds are chemically very strong and stable,
thus making them each a highly persistent substance (hence the term
POCs) under normal conditions. Due to their great lipophilicity and
high biostability, POCs are also very bioaccumulative in the environment.
From an environmental health perspective, POCs may be subsumed under four
major families: those structurally belonging to the chlorinated dioxin
family; those in the PCB family; those produced and used as
pesticides; and the majority others not readily classifiable into
any one of the first three. |
